What role does the pilot light play in a furnace? Though small, it is a crucial component in igniting the heat source and ensuring the heating system operates correctly. Let us explore how these ignition systems work, common problems, and how technicians resolve them.
Understanding the Role of Pilot Lights
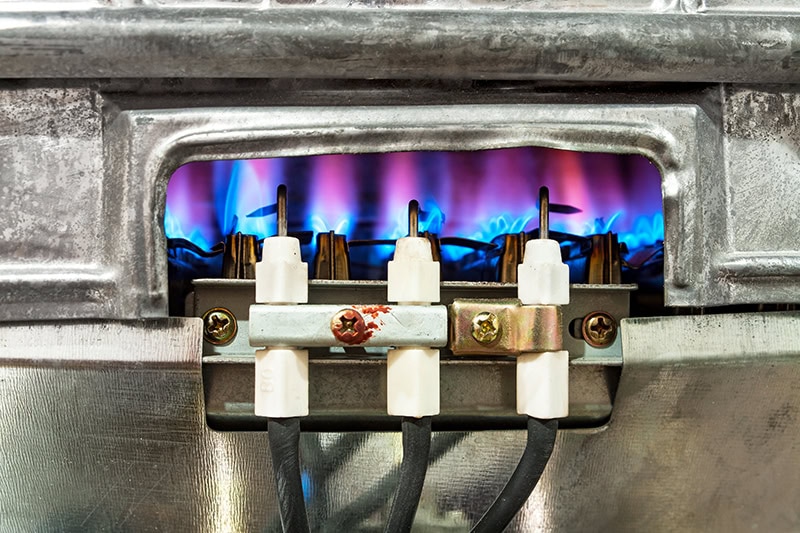
In older heating systems, the standing pilot light is a small flame that ignites the burners to produce warmth. This tiny flame remains on at all times, allowing for quick ignition when the system needs to heat the home. The ignition flame works in conjunction with the system’s gas valve to regulate the flow of gas, ensuring a controlled ignition process.
When the thermostat signals the need for heat, the flame ignites the main burner. Without a functioning ignition source, the burners cannot light, and the system will not generate warmth. This makes it essential to keep the heating unit operational during cold months.
Common Issues with Pilot Lights
The furnace can experience several common issues, often leading to problems with heating. A weak or flickering flame can indicate problems with the furnace. If the flame goes out frequently, it could signal a gas supply problem or a malfunctioning component, such as the thermocouple, which regulates gas flow.
Another frequent issue is a dirty or blocked ignition tube. Over time, dust and debris can accumulate, disrupting the flow of gas to the flame. This can cause it to burn irregularly or fail to stay lit. When these issues occur, prompt attention is necessary to prevent further malfunctions in the heating system.
How Technicians Diagnose Furnace Problems
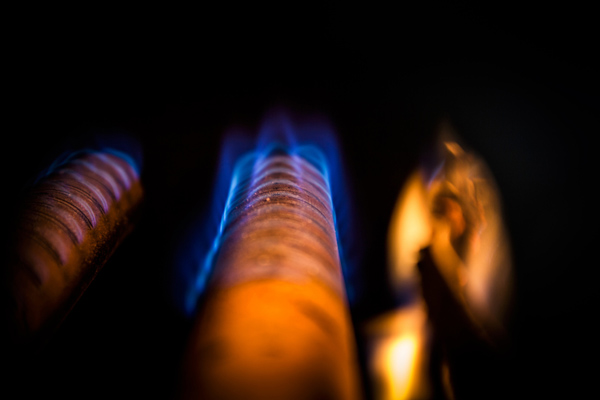
When called to fix an ignition issue, professionals follow a systematic process to diagnose the problem. First, they inspect the flame itself to determine if it is burning brightly and consistently. A healthy ignition source should be blue, with a strong, steady burn. Any variations, such as a yellow or flickering flame, can indicate a problem.
Next, they check the thermocouple, a safety device that detects whether the flame is lit. If this component is faulty, it may cut off the gas supply, causing the pilot to go out. Technicians also inspect the gas valve and ignition tube for blockages or other issues that could disrupt the gas flow.
Fixing Common Furnace Issues
Once the problem is identified, professionals proceed with repairs. If the flame is weak or not staying lit, they may clean the ignition tube to remove any blockages. A blocked tube can reduce gas flow, preventing the ignition flame from burning steadily. Cleaning the tube can often restore proper functionality.

This device plays a vital role in safety, as it shuts off the gas if the flame goes out. Replacing a faulty thermocouple ensures that the heating unit can operate safely and efficiently. In some cases, technicians may also adjust the flame by regulating the gas flow to the ignition source.
Key Safety Considerations
Safety is a top priority when dealing with ignition systems and gas heating units. Technicians take extra precautions to prevent accidents.
Important safety tips for handling gas heating systems include:
- Ensure proper ventilation around the unit
- Regularly check the flame for proper color and strength
- Avoid trying to relight the system without professional guidance
- Schedule regular maintenance to keep the system in good condition
- Immediately address any strange odors, such as gas or burning smells
Ignition systems, such as the standing pilot light, play a critical role in the operation of heating units, and when problems arise, professionals are trained to diagnose and fix them efficiently. By understanding the function of the furnace, technicians can restore heating systems quickly and safely. Keeping the ignition system in good condition through regular maintenance ensures the heating unit operates smoothly, providing warmth and comfort when it is needed most.